Aelf is a customizable operating system (OS) specifically for blockchains. The team is aiming for it to be the “Linux system” of the blockchain community.
As you probably know, blockchain adoption and innovation are advancing exponentially. First, Bitcoin paved the way as a peer-to-peer digital currency. You can think of it as a simple app. Next, Ethereum made it possible to build specific decentralized apps (DApps) through smart contracts – basically an app platform. However, this still falls short of the robust operating systems, like Windows, MacOS, and Linux, we’re using today.
Our current operating systems are incapable of efficiently running DApps while current blockchains have their drawbacks as well. They’re not scalable, can have interference in smart contract execution, and lack a consensus protocol to smoothly incorporate new technology. Aelf solves these problems.
In this aelf guide, we’ll talk about:
- How Does Aelf Work?
- Aelf Token (ELF) Supply
- Aelf Team & Progress
- Trading
- Where to Buy ELF
- Where to Store ELF
- Conclusion
- Additional Aelf Resources
How Does Aelf Work?
To solve the problems with current blockchain technology, aelf focuses on two primary innovations: side chains and a unique governance system. The project segregates resources and smart contracts through the use of side chains to improve scalability while utilizing a Delegated Proof-of-Stake consensus system for more adaptable governance. Let’s dive deeper into each of these.
Side Chains
Aelf consists of one main chain and numerous side chains to run the smart contracts on the platform. The main chain is the backbone of the entire system and is also capable of interacting with outside chains. Each side chain is dedicated to a specific type of smart contract. Side chains are unable to interact with each other, so they must communicate through the main chain when transmitting information.
All side chains are connected to the main chain through a side chain index system. The index system categorizes chains into two groups:
- External chains of high importance (Bitcoin, Ethereum, etc..)
- Internal side chains in the aelf OS
For example, the main chain could have Bitcoin branching off as one chain, a side chain for asset exchanges, and another chain breaking off for other asset types. Additionally, side chains can branch again into sub chains. To take out example further, the “other asset types” chain could have a sub chain for each type of asset and each of those chains could be broken down even further.
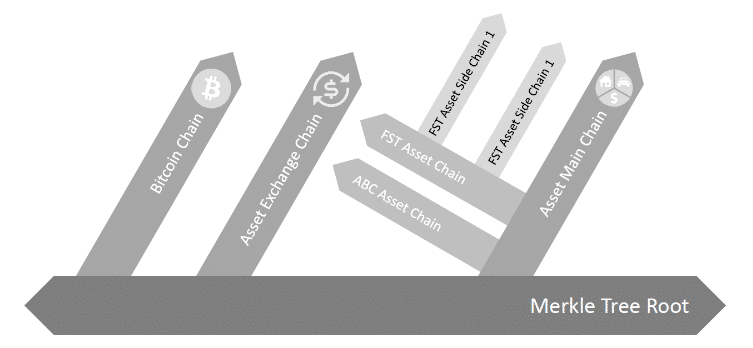
This strategy is similar to Ethereum’s sharding technique and should help the network efficiently scale. Separating the ecosystem into side chains ensures that bloating in one area won’t affect the entire network.
Token Ecosystem
Side chains need to pay a transaction fee to the main chain for indexing. The more a side chain contributes to the ecosystem, the less of a transaction fee it needs to pay. Bitcoin, with its widespread adoption, isn’t charged a fee. Side chains can also charge fees to any subchains that are attached to them.
Consensus Protocol
Because aelf nodes need to record information from numerous side chains onto the main chain, a normal Proof-of-Work (PoW) or Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus algorithm won’t suffice. Instead, the aelf main chain uses Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS), similar to Ark, to maintain the network.
As an aelf token (ELF) holder, you vote on which nodes become mining nodes. In return, the elected nodes decide how to distribute mining bonuses to the other nodes and stakeholders.
Aelf determines the number of network miners by the equation:
Miners = 2N + 1
Where “N” starts at 8 and increases by 1 each year. These mining nodes are responsible for relaying and confirming transactions, packaging blocks, and transferring data.
Aelf recommends that any chain created through the aelf OS merge their mining with the main chain and develop their own consensus protocol. Encouraging side chains to use their own consensus protocol enables them to customize it for their specific purpose.
[thrive_leads id=’5219′]
Aelf Token (ELF) Supply
In December 2017, the aelf team held a token sale for the platform’s ELF token to private investors. The team distributed 250,000,000 (25%) of the 1,000,000,000 total supply during this sale. The remaining tokens are for the following people/tasks:
- 250,000,000 (25%): Aelf Foundation, 3 year vesting period
- 160,000,000 (16%): Aelf Team, 2 year vesting period
- 120,000,000 (12%): Marketing/Air Drops, 3 year period
- 120,000,000 (12%): Mining, 100 year period
- 100,000,000 (10%): Advisors/Partnerships, 2 year vesting period
The mining rewards will decrease over a linear gradient across the 100 year period. As of this writing, 280,000,000 ELF are in circulation.
Aelf Team & Progress
Aelf was founded by Ma Haobo. Haobo was previously the founder/CEO of Hoopox as well as the CTO of GemPay and AllCoin. J. Michael Arrington, founder and CEO of TechCrunch, and Zhou Shouji, founding partner of FGB Capital, support the team as members of their advisory board.
Most notably, though, the project has received considerable investment from numerous venture capital firms. Draper Dragon, Blockchain Ventures, FGB Capital, and over 10 other investment firms participated in the token sale. In fact, the project has been so popular that the team had to turn down the majority of interested investors after reaching their 55,000 ETH goal within two weeks of starting the sale.
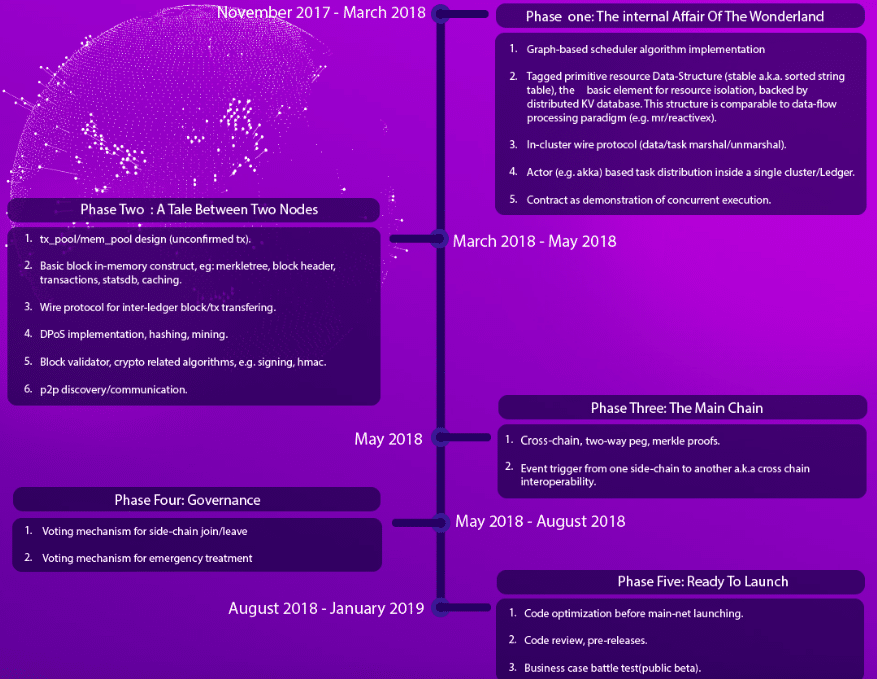
Still a young project, the aelf team is in the process of building out their product. Since the token sale, though, they’ve formed partnerships with Decent, Theta, and U Network. They’ve also accomplished a good chunk of their roadmap in a timely manner.
In June 2018, the team launched the project’s test net. And, in Septemeber the same year, they finished developing side chain capabilities. This update included side chain creations, indexing, and cross-chain interoperability. The main net launch is still scheduled for early 2019, and the team has shown no reason why they would miss this deadline.
Competitors
As a DApp platform, aelf competes with numerous other projects in the blockchain space. Ethereum and EOS are the two most notable competitors and are the furthest along in terms of development. Lisk and ICON may be the most similar to aelf in that they both use side chains in an effort to build their DApp ecosystem.
Trading
Aelf began trading in December 2017 and its price has had a turbulent run since then. Following the token sale, the ELF price rocketed up from around $0.87 (~0.000068 BTC) to an all-time high, in USD, of $2.61 (~0.000165 BTC). This increase was most likely caused by investors simply finding out about the coin. Because the project didn’t have a public ICO, it went under the radar as it hit exchanges.
Since the beginning of 2018, the ELF price has risen and fallen dramatically between these two price points. In this 2018 bear market, the price hit a low of about $0.45 (~0.000061 BTC) in March before launching up to hit an all-time BTC high (~0.000224 BTC) at the beginning of May. The rise coincided with the coin’s listing on Bithumb as well as the team’s implementation of a community promotional program. Since touching that mid-year high, though, the price has consistently fallen, currently sitting at an all-time low of around $0.14 (~0.000032 BTC).
As with most platform-based coins, product launches and news of notable partnerships should have a positive effect on the price. Be on the lookout for news of the main net launch towards the beginning of 2019 as this will most likely have an influence on the price as well.
Where to Buy ELF
There are two major exchanges where you can purchase ELF: Binance and Huobi. On Binance, you can exchange BTC and ETH for ELF while on Huobi you can trade BTC, ETH, and USDT. Check out our guides on how to buy Bitcoin and buy Ethereum if you’re not sure where to start.
Aelf also has a rewards system – Candy. With the Candy rewards system, you earn points, convertible for ELF, by accomplishing simple, daily tasks. Tasks include liking and replying to aelf tweets, inviting people to the Telegram channel, and other promotional activities.
Where to Store ELF
ELF is currently an ERC20 token. As such, you can store it in any wallet with ERC20 support like MyEtherWallet or Exodus. The Ledger Nano S is also a great option if you’re interested in additional security.
Once aelf launches the main net, though, ELF tokens will switch from Ethereum to the aelf main chain. This means that you may have to switch which wallet you store your funds in. Additionally, there may be extra steps you need to follow in order to exchange your ERC20 tokens for the ELF coins on the new blockchain.
Conclusion
Aelf is a relatively new competitor in the DApp platform race but already has solid support from large investment capital firms. The project is utilizing resource separation through side chains and a unique governance model to build an entire blockchain operating system.
Although further back than similar projects, aelf could benefit from the synergy created by the openness and scalability of its architecture. Only time will tell if it’s too little, too late for this up-and-coming coin.
Editor’s Note: This article was updated by Steven Buchko on 11.21.2018 to reflect the recent changes of the project.
Additional Aelf Resources
Never Miss Another Opportunity! Get hand selected news & info from our Crypto Experts so you can make educated, informed decisions that directly affect your crypto profits. Subscribe to CoinCentral free newsletter now.