TLDRs:
- China could operate 300,000 driverless taxis in major cities by 2030, UBS predicts.
- Robotaxis may reach 4 million nationwide by the late 2030s, boosting productivity.
- Autonomous taxis could generate over $40 billion annually in China’s initial market.
- Low production costs and government support accelerate robotaxi adoption nationwide.
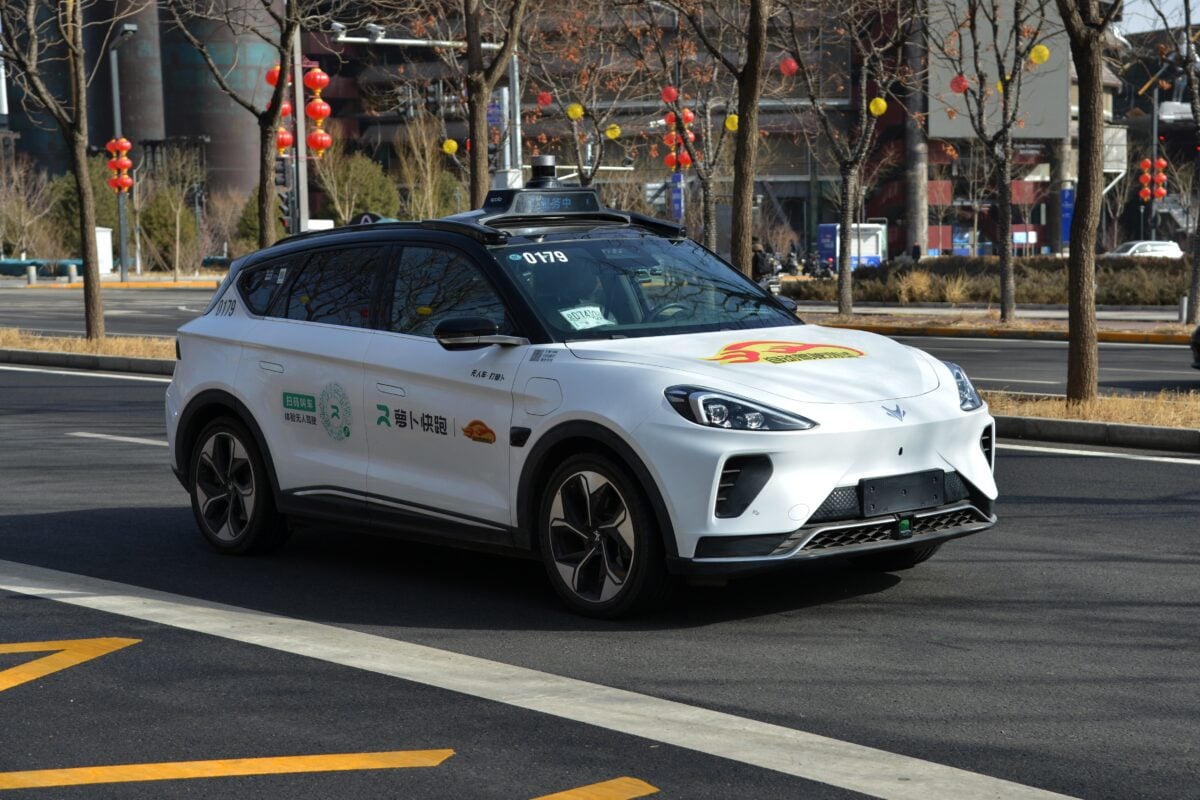
China is on the verge of a transportation revolution. According to a recent UBS forecast, the nation could see 300,000 driverless taxis operating in its four top-tier cities by 2030, with numbers potentially reaching 4 million by the late 2030s.
The growth of autonomous ride-hailing services, or “robotaxis,” is being driven by rapid advances in artificial intelligence (AI) and the strength of China’s electric vehicle (EV) industry.
AI and EVs Power Robotaxi Growth
UBS analysts note that China’s robust AI capabilities, combined with a highly competitive local EV market, are key factors supporting the rise of driverless taxis.
Paul Gong, head of China automotive research at UBS, explained that autonomous vehicles could significantly boost productivity as labor costs increase and technology continues to evolve.
“Given the fast development of technologies and the increasingly expensive labour cost, autonomous vehicles will be highly helpful in driving productivity,” he said.
He projected that replacing all taxis and ride-hailing cars with self-driving cabs could create a market worth up to $183 billion annually, though the full commercial rollout timeline remains unclear.
HSBC has also weighed in, estimating that autonomous taxis could account for roughly 6% of China’s taxi market, with an initial market value exceeding $40 billion per year.
The financial potential expands further when factoring in logistics and delivery services, which could add an additional $30 billion annually. These projections underscore the enormous economic opportunity that robotaxis present for China.
Cost Advantage Drives Rapid Adoption
One of the major advantages China has in scaling robotaxis is cost. UBS predicts that the production cost for a self-driving taxi in China could fall below 300,000 yuan (approximately $41,900).
This contrasts sharply with costs in other regions, particularly the United States, where rides can be nearly six times more expensive. Currently, robotaxi rides in China average about 35 cents per mile, compared to $2 per mile in the U.S., an 83% cost advantage.
This economic efficiency is fueled by China’s highly competitive automotive supply chain and government subsidies, enabling companies to deploy fleets faster and achieve sustainable unit economics. Affordable pricing also broadens access, allowing more consumers to embrace autonomous ride services, which accelerates mass adoption.
Government Coordination Supports Expansion
China’s ambitious robotaxi growth is not accidental. The government has systematically prioritized autonomous vehicle development since 2017. A comprehensive national plan established testing-friendly policies in over 50 cities and standardized critical communication and electronics systems essential for AV operations.
The coordinated effort has already produced measurable results. Baidu’s Apollo Go, China’s leading robotaxi operator, has completed over 11 million rides, surpassing U.S.-based Waymo, despite starting later. This demonstrates the effectiveness of China’s “top-level design” approach, which aligns government policy with technological progress across multiple administrative levels.
Looking Ahead
As production costs continue to decline and AI technology advances, China’s driverless taxi market is poised for explosive growth. By the late 2030s, millions of autonomous taxis could be operating nationwide, transforming urban mobility, reducing labor dependency, and creating substantial economic value.
With government backing, technological expertise, and cost efficiency all converging, China is on track to lead the global robotaxi market.