With over 3,500 decentralized applications, Ethereum has established itself as the top choice for blockchain developers. However, a slew of competitors (new and old) are looking to capitalize on Ethereum’s growing pains– projects like Polkadot, Cardano, and Solana are eager to succeed where Ethereum has performed poorly.
If Ethereum wants to stay competitive, the Ethereum 2.0 Upgrade must first address its all-time high gas fees (~$5.75/transaction) and its relatively slow transaction speeds (10-15 transactions/second).
These two factors make it 1,000,000x more expensive to develop on the Ethereum blockchain than a centralized network.

Vitalik Buterin, the co-founder of Ethereum, and his team have been working to address these concerns, but have yet to make sizable changes to the current blockchain known as the mainnet. The new Ethereum 2.0 Upgrade, however, may be exactly what the Ethereum project needs.
This upgrade will address the current scalability, security, storage, and sustainability needs of the network. The three stages are:
- The Beacon Chain
- The Merge
- The Shard Chains
Beacon Chain
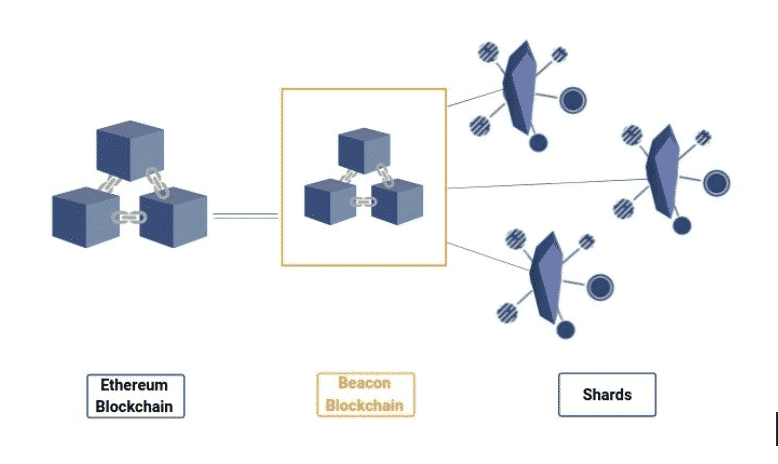
The first stage of the Ethereum 2.0 Upgrade was already released in December 2020. The Beacon Chain will take over the role as the main hub from the Ethereum mainnet and handle data storage, on-chain security, and block validation.
It will also transition Ethereum over from a Proof-of-Work model to Proof-of-Stake.
Proof-of-Work, the current model, involves validators mining blocks and securing transactions that reward them in ETH. This process can have a negative impact on the environment and push out potential validators that don’t have the computing power to handle solving complex problems.
The Beacon Chain, according to the Ethereum team, will help usher in a more scalable solution in the long term with this Proof-of-Stake model that will be discussed in the next phase.
However, the role of the Beacon Chain still won’t handle more complex computations like the execution of smart contracts, which is currently conducted on the mainnet.
It will simply act more as a way to introduce staking to the network and randomly assign validators to the new shard chains in Phase Three.
Merge: When Will Ethereum Go to Proof of Stake?
Once the Beacon Chain is secure, the current Ethereum mainnet will merge with the Beacon Chain. This will mark the full transition to a Proof-of-Stake system from Proof-of-Work.
Even though the marriage of the two systems isn’t expected to happen for another six to twelve months, both systems are still currently running in parallel.
Once the merge commences, the mainnet will become one of the shards on the beacon chain. We’ll discuss shards in the next phase, but this is important because the mainnet will bring with it the ability to execute smart contracts on the beacon chain.
At this point, mining will no longer be necessary to run the ecosystem.
Ethereum’s switch over to Proof-of-Stake will eliminate the need for mining in favor of a system focused on a network of validators. Validators will be required to stake 32 ETH tokens on the Beacon Chain in order to be randomly assigned to validate blocks.
Staking is imperative for increasing overall network security and reducing the chance of foul play. If a validator is caught, their 32 ETH will be taken by the network.
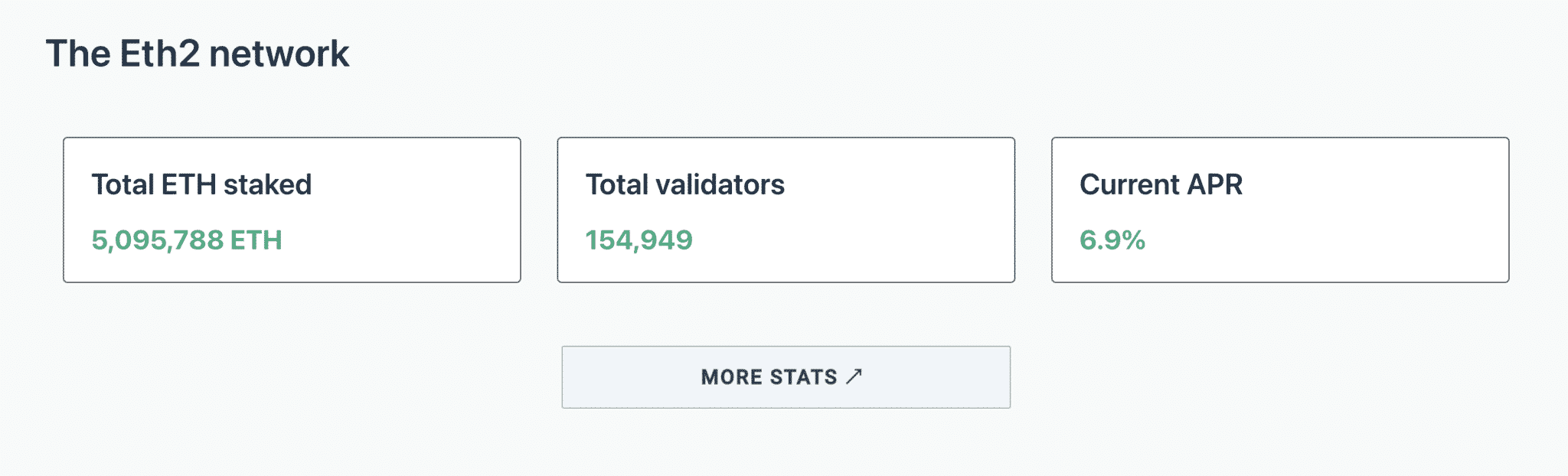
Currently, there is around a 7% APR for validators that stake their ETH on the network and Ethereum 2.0 may still consider validators that have less than 32 ETH.
Ethereum Shard Chains
The final piece of the puzzle with Ethereum 2.0 is splitting the existing Ethereum database to spread the load in a process called “sharding”.
The Ethereum 2.0 upgrade plans to add around 64 new shards to the Beacon Chain starting at the end of 2021.
These shard chains will help:
- Reduce validator workload by only having to validate one shard rather than the entire network
- Mitigate threats to the network by reducing the scale of the threat to just that shard
- Speed up transaction time and reducing hardware costs/requirements
The majority of the shards will be for data storage, but the Ethereum Foundation has discussed repurposing some shards for the greater good of the network. This may even include shards that can handle the execution of smart contracts similar to the mainnet shard.
Final Thoughts: Ethereum 2.0 or Bust?
It’s a tough task to go from 10 transactions/second to 100,000 transactions/second, but the Ethereum 2.0 Upgrade is a step in the right direction.
The Beacon Chain is currently running in parallel to the mainnet, but the merge will be happening closer to the end of 2021. Once the mainnet becomes a shard on the Beacon Chain and more shards are added, the Beacon will ensure the shards are synchronized and secure.
Ethereum will likely provide its developers and the users of its myriad applications (NFTs, DeFi, etc) a much better experience with its 2.0 rendition. Is Ethereum 2.0 as big of an event as it seems, or is it just marketing hype? Only time will tell.