TLDR
- Nvidia to share 15% of China H20 chip revenue with U.S., worth up to $3B.
- Deal follows April export ban reversal by Trump administration.
- China accounts for 13% of Nvidia’s total revenue.
- Analysts warn levy could pressure margins but secures market presence.
- AMD also part of the agreement, impacting both companies’ China sales strategy.
Nvidia Corporation (NASDAQ: NVDA) traded at $182.79, up 0.03% as of 2:47 PM EDT Monday, after news broke that the company reached an unprecedented revenue-sharing deal with the U.S. government to maintain its business in China.
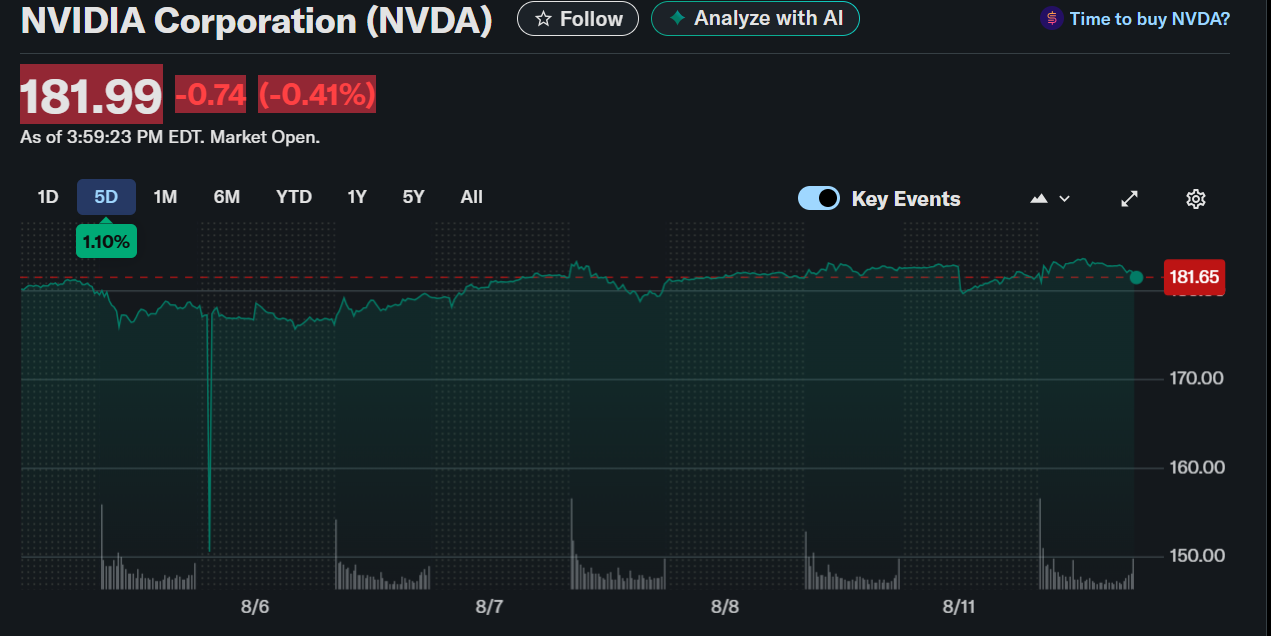
The agreement requires Nvidia to pay 15% of revenue from H20 chip sales in China, potentially amounting to $3 billion for the current fiscal year ending January 2026.
The Agreement and Its Origins
President Trump confirmed the deal during a press briefing, calling Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang “a brilliant guy.” The arrangement follows an April ban on H20 chip exports to China, which cost Nvidia billions in lost sales before being reversed in July. In exchange for export licenses, both Nvidia and rival Advanced Micro Devices (AMD) will share revenue from Chinese sales.
JUST IN:
Nvidia $NVDA and $AMD have reportedly agreed to share 15% of the revenues from H20 chip sales in China 🇨🇳 with the United States 🇺🇸 Government – Financial Times pic.twitter.com/igGrPHPItG
— Evan (@StockMKTNewz) August 10, 2025
A White House official verified the 15% levy, while analysts described the arrangement as unusual and possibly unconstitutional, citing concerns over the U.S. Constitution’s ban on export taxes. Trade policy experts also questioned whether the decision was compromising national security for financial gain.
Market Impact and Strategic Concerns
China represents 13% of Nvidia’s total revenue, with $17 billion earned there in the last fiscal year. The H20, based on Nvidia’s Hopper architecture, has been a key product for the Chinese market. The company has also launched Blackwell-based chips to comply with U.S. export restrictions, aiming to retain customers and deter them from shifting to domestic alternatives such as Huawei.
While the agreement ensures continued access to the Chinese market, analysts warn that it could pressure gross margins for Nvidia and AMD by 5 to 15 percentage points on affected products. DA Davidson’s Gil Luria cautioned that the arrangement may prompt China to accelerate development of domestic chip suppliers to avoid revenue flows to the U.S.
Political and Industry Reactions
The Trump administration defended the deal, claiming it did not jeopardize national security. U.S. Commerce Secretary Howard Lutnick described the H20 as Nvidia’s “fourth-best chip” and stressed the importance of keeping Chinese firms dependent on U.S. technology. However, former Commerce Department adviser Alasdair Phillips-Robins criticized the move, arguing it traded national security protections for Treasury revenue.
Bernstein analyst Stacy Rasgon suggested the deal was still preferable to blocking sales entirely, as it prevents Huawei from dominating the Chinese AI chip market. AMD, which generated $6.2 billion in China in 2024 (24% of its total revenue), is also participating in the levy as a condition for export licenses for its MI308 chips.
Earnings Outlook
Nvidia’s earnings date has not been officially confirmed but is expected in early 2026, covering its fiscal year ending January 2026. Wall Street forecasts suggest the company could recover $15 billion in lost sales in the second half of the year, bringing Chinese revenue to around $20 billion despite the levy.