What is Plasma for Ethereum?


Plasma is a framework to scale Ethereum blockchain’s processing power, and the brainchild of Vitalik Buterin, co-founder of Ethereum, and Joseph Poon. Prior to this project, Joseph Poon collaborated with Thaddeus Dryja to develop Plasma’s Bitcoin equivalent of Lightning. Both frameworks are trustless and multilayered networks. Trustless means users do not need to know or trust counterparties to make a transaction. Poon and Buterin developed Plasma to facilitate a decentralized market for the general public to purchase not only tokens and cryptocurrencies but real goods and services.
Currently, Ethereum can process approximately 15 transactions per second, in comparison to Bitcoin’s 7 transactions per second. Both platform’s processing capacities pale in comparison to Visa’s ability to manage 45,000 transactions per second. Plasma promises to enable Ethereum to scale up its processing capacity to thousands or potentially billions of transactions per second.

How does Plasma Work?
Plasma provides security and scalability by allowing subsidiary “child” blockchains to branch off of the main “parent” blockchain. These child blockchains facilitate micro-transactions to process faster and at a cheaper rate. Blockchain children can coexist and function independently from the parent blockchain and each other.
Blockchain platforms use a network of nodes to store the state of account balances, contracts, and storage. Miners cross-reference these decentralized nodes to validate that blockchain records match and contain no errors or fraud. This process is accurate and fairly secure.
 Poon, J., & Buterin, V. (2017, August 11). Plasma [PDF].
Poon, J., & Buterin, V. (2017, August 11). Plasma [PDF].

Unfortunately, relying on one blockchain’s ledger grows more difficult as Ethereum hosts more transactions every day. As each node fills with more transactions and data storage, miners face greater difficulty verifying each transaction in a timely fashion. Over time, the blockchain begins to bottleneck while verifying large transactions and many micro-transactions are effectively booted off the blockchain.
Without the capacity to track smart contracts and trading on a global scale, cryptocurrency is not ideal for regular consumer purchases. Plasma relieves a great amount of bottleneck pressure from Ethereum’s ledger by letting child blockchains process the majority of the data and storage within the network.

Smart contracts on the Ethereum Blockchain live within the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), the part of Ethereum’s coded protocol that manages account updates and computation. EVM allows decentralized applications to run, safely protected from fraud, censorship, and third-party interference within its built-in programming language.
Smart contracts are transactions in which the rules, conditions, and payments are coded into an exchange between users’ crypto-wallets. Plasma uses EVM smart contracts, to protect runtime environments of the off-shooting “child” blockchains, maintaining Ethereum’s accuracy and integrity.
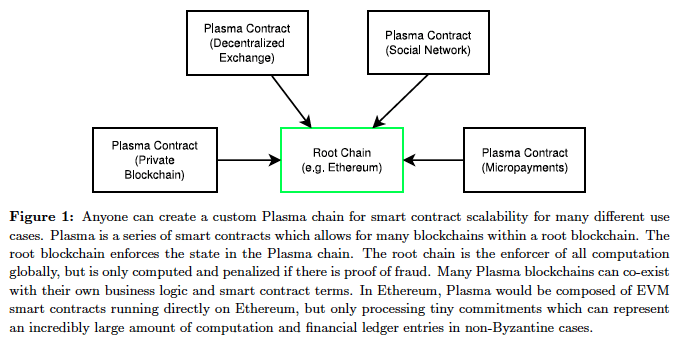
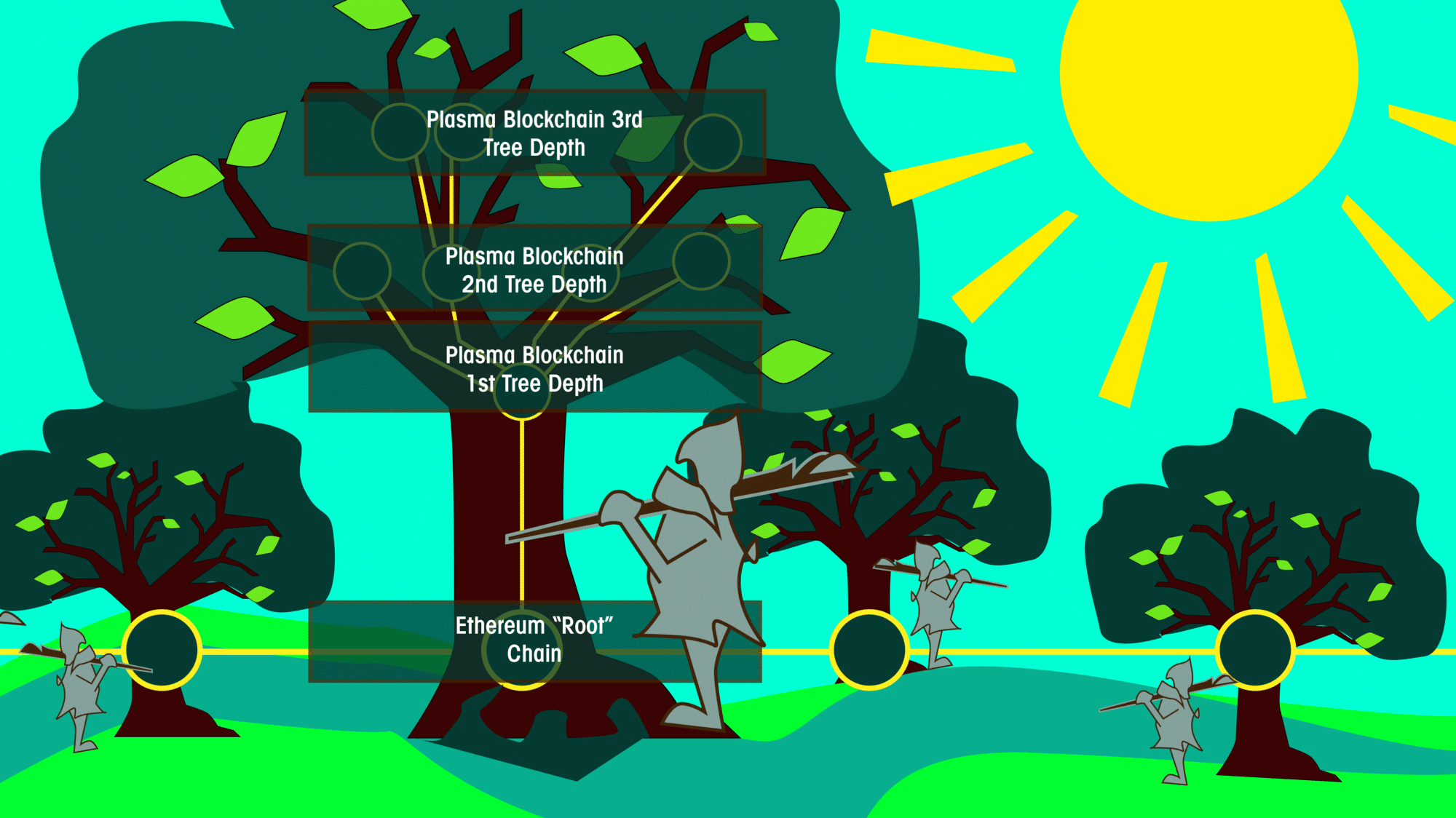
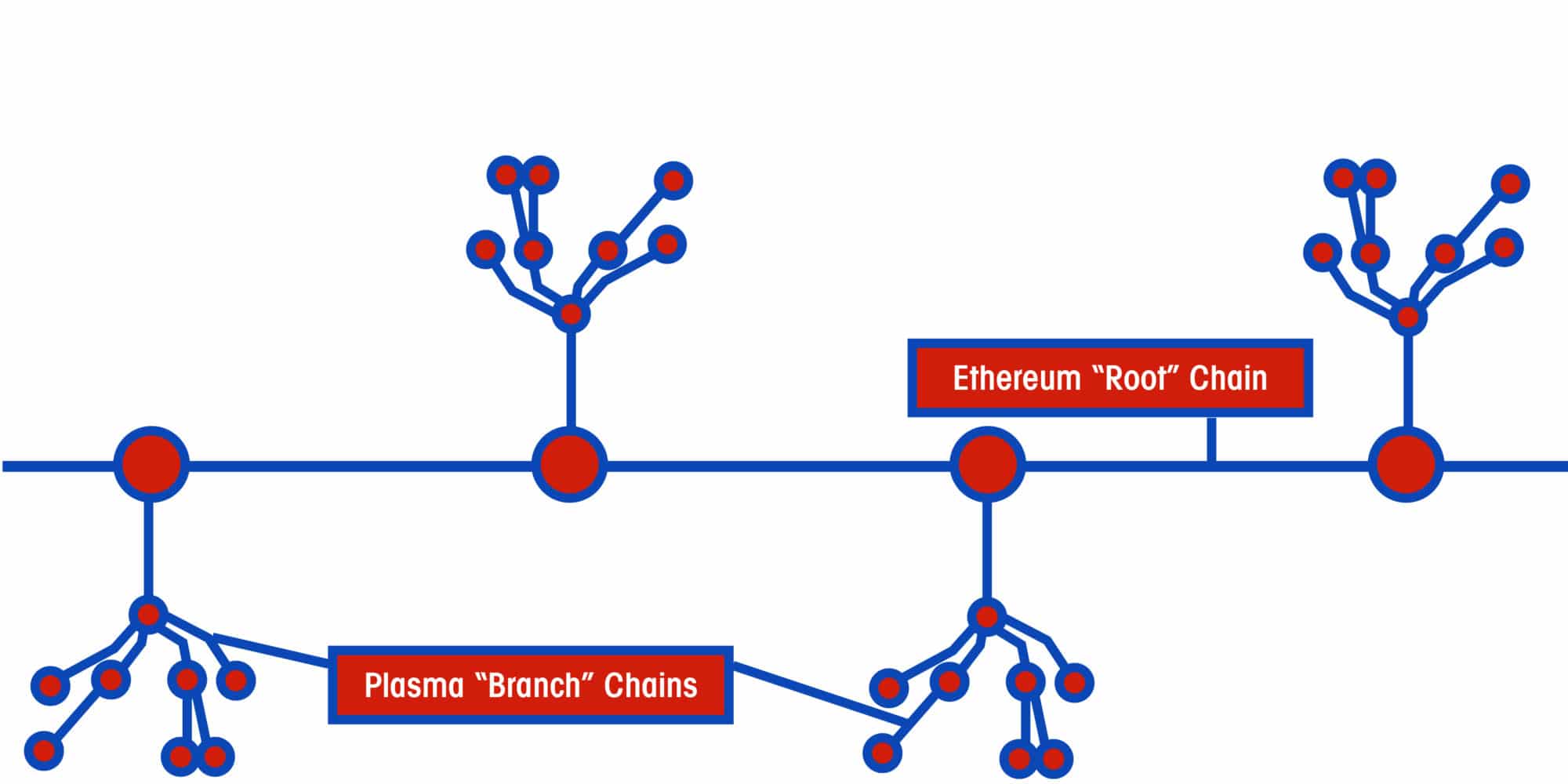
Plasma Tree Structure: Root and Branch Blockchains
In Plasma’s white paper, the framework structure looks like a tree with different levels of branches in a blockchain hierarchy. The white paper refers to the Ethereum’s main blockchain as the “root” or “parent” blockchain. Plasma blockchains branch from the “root” into second and third tier blockchains, or micro-transaction channels.

By further decentralizing the network of smart contracts and ledgers, Plasma facilitates more efficient and secure microtransactions. Users can execute smart contracts within the child blockchains without having to report each change of account states to the main Ethereum blockchain.
The tree metaphor, although graphically accurate, does not explain the nuanced, social, and financial system that allows users to leave the regulated blockchain safely and enter private, smart contract ecosystems of exchange.

Within a Plasma child blockchain, parties must both sign off on each transaction to verify each other’s new account balances before making an exchange. For example, I can enter a smart contract which states that I pay you a flat rate every time my banner ad gets clicked on your website. Each sale referred by your site triggers an additional commission payment. Funds are periodically transferred from my wallet to yours whenever a click or sale triggers the coded contract. After each exchange, we both confirm our account balances within our child blockchain.
The branched blockchain only sends data to the root chain if one of us wants to validate a state of accounts. If I decide to remove my ad from your website, I exit the smart contract child blockchain. The final state of accounts can be recorded on the parent blockchain but does not have to be.
Plasma Security
Each Plasma Blockchain can co-exist with its own business logic, contract terms, and triggering events using EVM smart contracts, without accessing the network file system or other processes. These blockchains can live within their own protected marketplace, relying on the Parent Blockchain to enforce fair exchange.
How do Child Blockchains Remain Secure?
Much like a neighborhood exists within a larger metroplex infrastructure, child blockchains live in the suburbs of key urban centers. These suburbs create space for users by providing microchannels for smart contract transactions. Incentivized validators maintain security within their smaller communities much like a neighborhood watch.
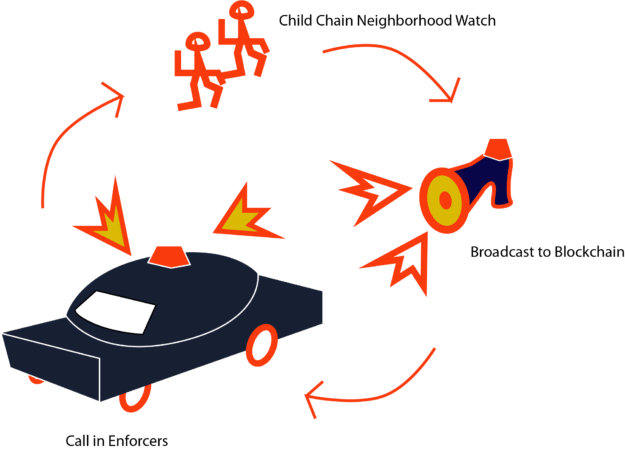
The police do not watch shopkeepers as they sell goods. The police do not patrol around to check-in on real estate agents as they broker purchases of homes. Similarly, each microchannel independently maintains ledgers and smart contracts without mining verification. “Local” validators are incentivized to work as watchmen for fraudulent behavior inside of their independent community.
If the watchmen detect a criminal (fraudulent behavior or hack), they can alert and evacuate the community from the neighborhood (child blockchain). Although watchmen do not have the power to enforce consequences, they can report the instance to the police station, which will bring the criminal to a court of law (parent blockchain).
Now, instead of a tree structure, imagine the US court system. There are Municipal Courts, State Courts, and a Supreme Court. Within Plasma, Ethereum is the Supreme Court. A hierarchy of Judicial Courts beneath it creates a well-balanced, secure system.
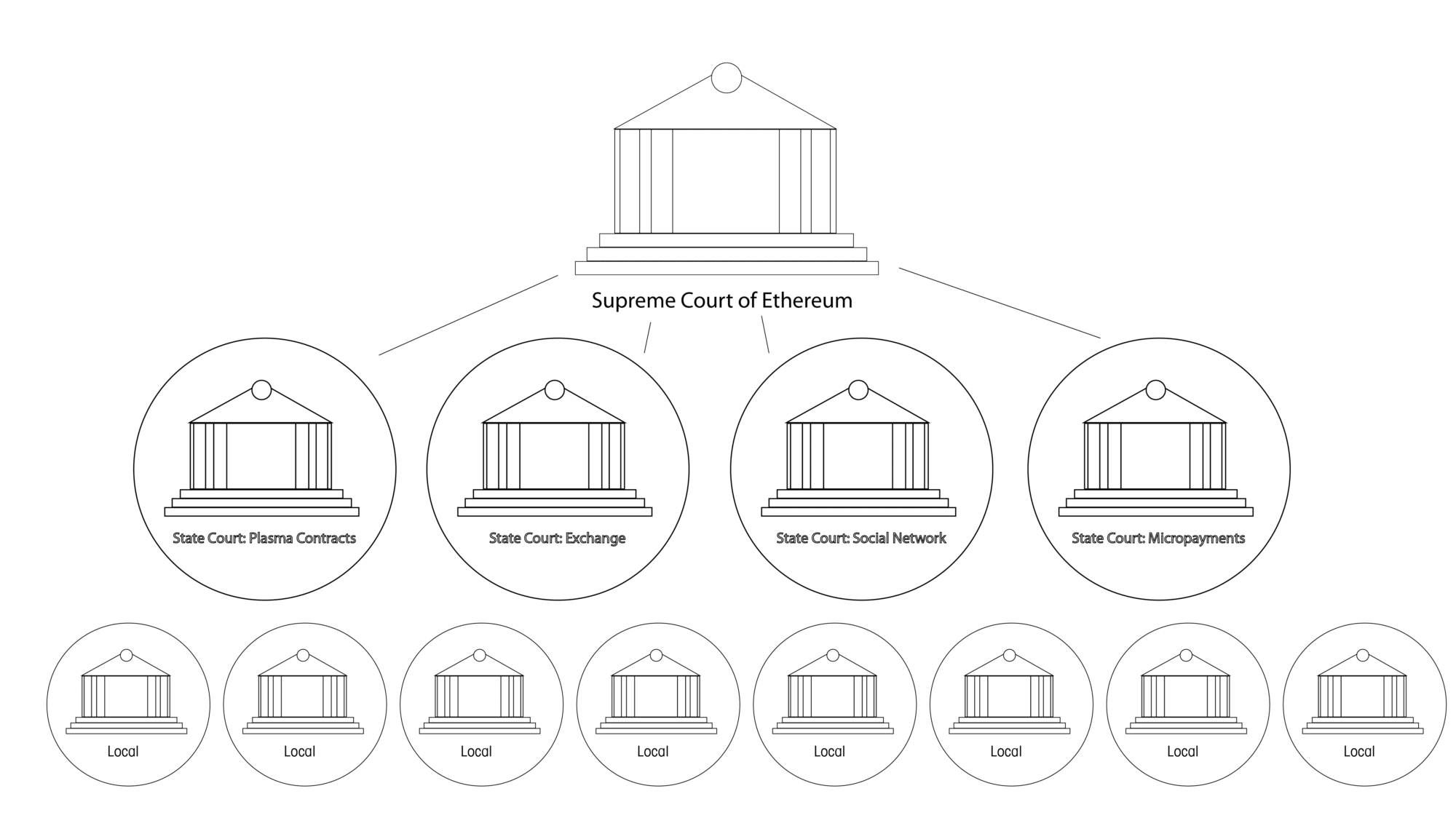
Using a hierarchy of security and enforcement allows people to go about their daily business transactions efficiently and relatively safely, reserving more official and important exchanges for the parent blockchain.
Plasma’s ability to increase Ethereum microtransaction efficiency paves the road for mainstream consumers to use blockchain technology for purchasing goods, banking, trading, and more.
Images by Ray Fontaine






