TLDRs;
- VinFast reported an $812M Q2 net loss, even as revenues jumped 91.6% year-on-year to $663M.
- EV deliveries surged 172% to 35,837 units, with scooters and e-bikes rising 432% to 69,580 units.
- The company expanded globally, opening showrooms in India, Indonesia, the Philippines, and its first U.S. dealership in California.
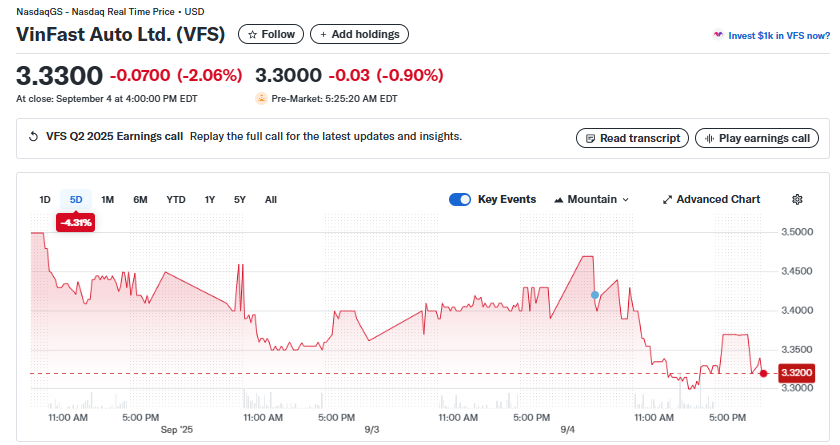
- Stock fell 2.06% to $3.33, reflecting investor concerns about steep losses despite strong sales momentum.
Vietnamese electric vehicle maker VinFast Auto Ltd. (VFS) reported a second-quarter 2025 net loss of $812 million, even as sales momentum accelerated. Revenues climbed 91.6% year-on-year to $663 million, driven by surging deliveries of both cars and two-wheelers.
The company delivered 35,837 EVs in Q2, a 172% jump from the previous year. Its e-scooters and e-bikes also saw dramatic growth, with 69,580 units sold, up 432% from 2024. Despite these gains, VinFast’s stock fell 2.06% on September 4, closing at $3.33.
Strong Home Market Foundation
VinFast has emerged as a dominant force in its domestic market. Models such as the VF 3, VF 5, and VF 6 ranked among Vietnam’s top five best-selling vehicles in the first half of 2025.
Over 70% of these deliveries were to individual consumers, reinforcing the brand’s mainstream adoption.
This strong foothold has given VinFast a foundation to pursue aggressive expansion abroad, even while operating at steep losses. The company ended Q2 with 394 showrooms worldwide, underscoring its ambition to grow beyond Southeast Asia.
Global Expansion Strategy
In India, VinFast opened its first dealerships in Surat and Chennai and began assembling the VF 6 and VF 7 at its newly established Tamil Nadu plant, which has an initial annual capacity of 50,000 vehicles.
Elsewhere, VinFast captured 25% of the EV market in the Philippines during H1 2025, while Indonesia accounted for 5% of quarterly deliveries.
In the United States, VinFast signed its first authorized dealership agreement with Sunroad Automotive Group, opening a showroom in San Diego in August 2025.
Scale Remains the Biggest Hurdle
While sales growth has been impressive, VinFast’s financials highlight the high cost of scaling an EV business. Its gross margin improved from negative 62.7% in Q2 2024 to negative 41.1% this year, signaling progress but still far from profitability.
VinFast, $VFS, Q2-25. Results:
📊 EPS: –$0.35 🔴
💰 Revenue: $663M 🟢
📈 Net Loss: $812M
🔎 EV and e-scooter deliveries remained strong as VinFast continued to scale, backed by improving gross margins and expanding global reach. pic.twitter.com/aJnQUEphIn— EarningsTime (@Earnings_Time) September 4, 2025
Executives have drawn parallels to Tesla’s early years, prioritizing “scaling volumes while being disciplined on costs” over short-term profits. Analysts expect annual losses to exceed $3.2 billion in both 2024 and 2025, reflecting the capital-intensive nature of EV manufacturing.
The company continues to invest heavily in infrastructure, with more than $2 billion allocated to the Indian market. Management argues that these moves are essential for long-term competitiveness, even at the expense of current financial pain.