- Be Weary of Cryptocurrency Giveaways
- “Guaranteed Returns” on ICOs
- Cloud Mining Scams
- Don’t Go Phishing
- Conclusion
While the cryptocurrency market can be a good way to make money, it is also a prime target market for scammers. In this article, we’ll look at some of the most common bitcoin schemes and how to protect yourself from falling for them.
Be Weary of Cryptocurrency Giveaways
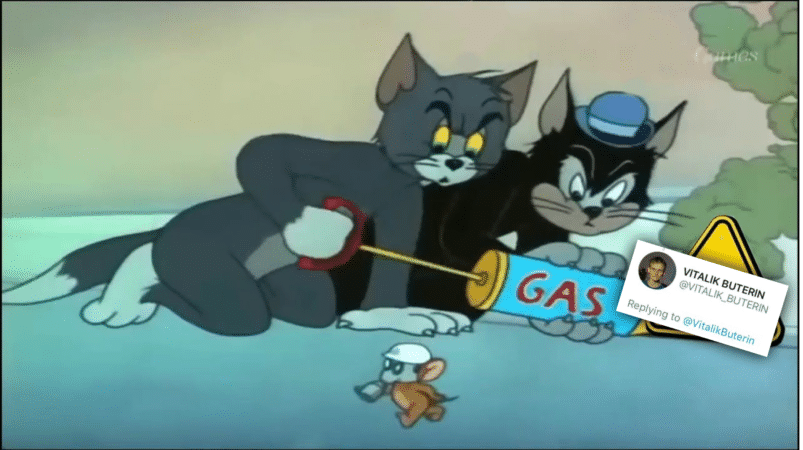
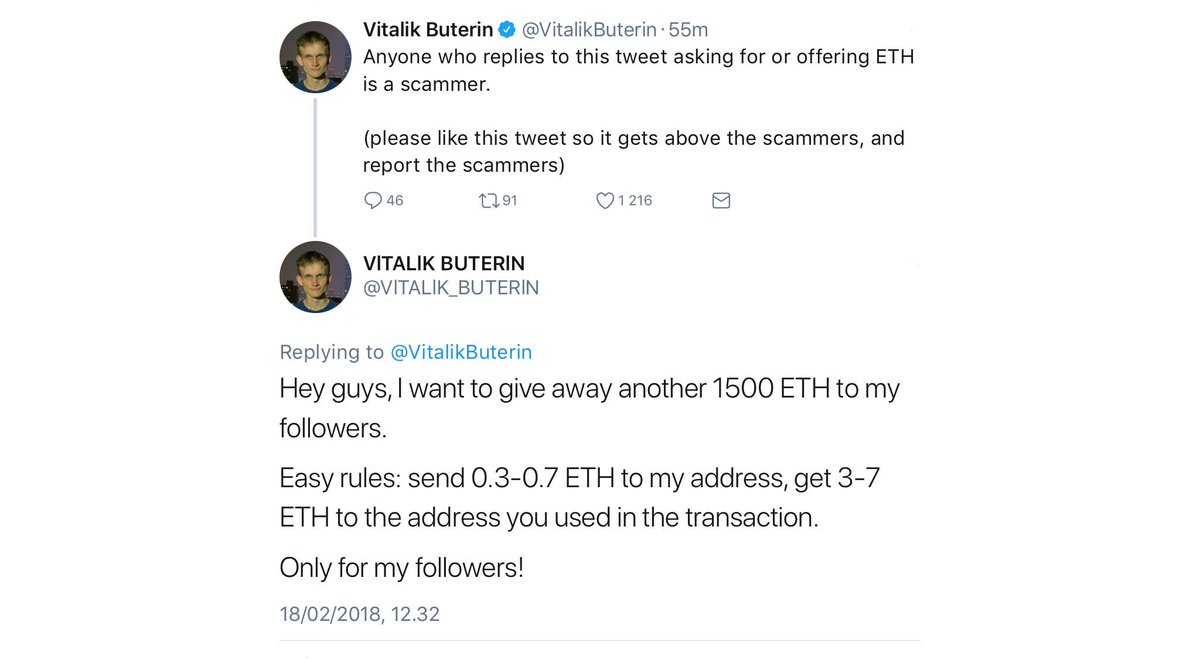
Amongst the various types of bitcoin schemes, many of the top people and projects in the industry are concerned with the prevalence of giveaway scams. These scams often take place on popular social media platforms, especially Twitter. Big names like Vitalik Buterin even list “Not giving away ETH” in their profiles to make the cryptocurrency community aware of this issue.
Typically, these scams will tell people to send ETH or BTC to a given address. The scammer promises to give that person more ETH or BTC in return. While this might seem like an obvious scam, the number of profiles that include “Not giving away ETH” make it apparent that this type of scam is quite rampant.
Even in the case of legitimate airdrops or bounty programs, the amount of funds given away are typically much lower. Most importantly, legitimate giveaways would never ask a user to send funds first and then give funds in the same cryptocurrency back.
“Guaranteed Returns” on ICOs
In some financial markets (i.e. bonds, CDs, etc.), banks guarantee returns of a certain amount. However, this is not the case in other financial markets. Much like in the stock market, the cryptocurrency market has no profit guarantees. Any cryptocurrency ICO that guarantees that the price of its token will rise to a certain percentage is likely to be a scam. ICO scams continue to be a problem for the cryptocurrency market, especially due to the lack of regulatory frameworks throughout the world.
Even if it is very possible that a given cryptocurrency will rise in value over time, scams are likely to use precise numbers and phrases like “guaranteed returns”. Similar to the giveaway scam, these ICOs will ask investors to send BTC, ETH, or other popular cryptocurrencies to the scammer’s wallet address.
The problem is that almost every cryptocurrency project (legitimate or not) relies upon this type of exchange of funds. The only major difference, in the end, is that a scam doesn’t send tokens in return.
So what separates ICO scams from legitimate ICOs?
While some fake projects guarantee returns, legitimate ones do not. Legitimate ICOs typically have several positive reviews, verified team members with KYC and AML checks, established strategic partnerships, and other factors.
Cloud Mining Scams
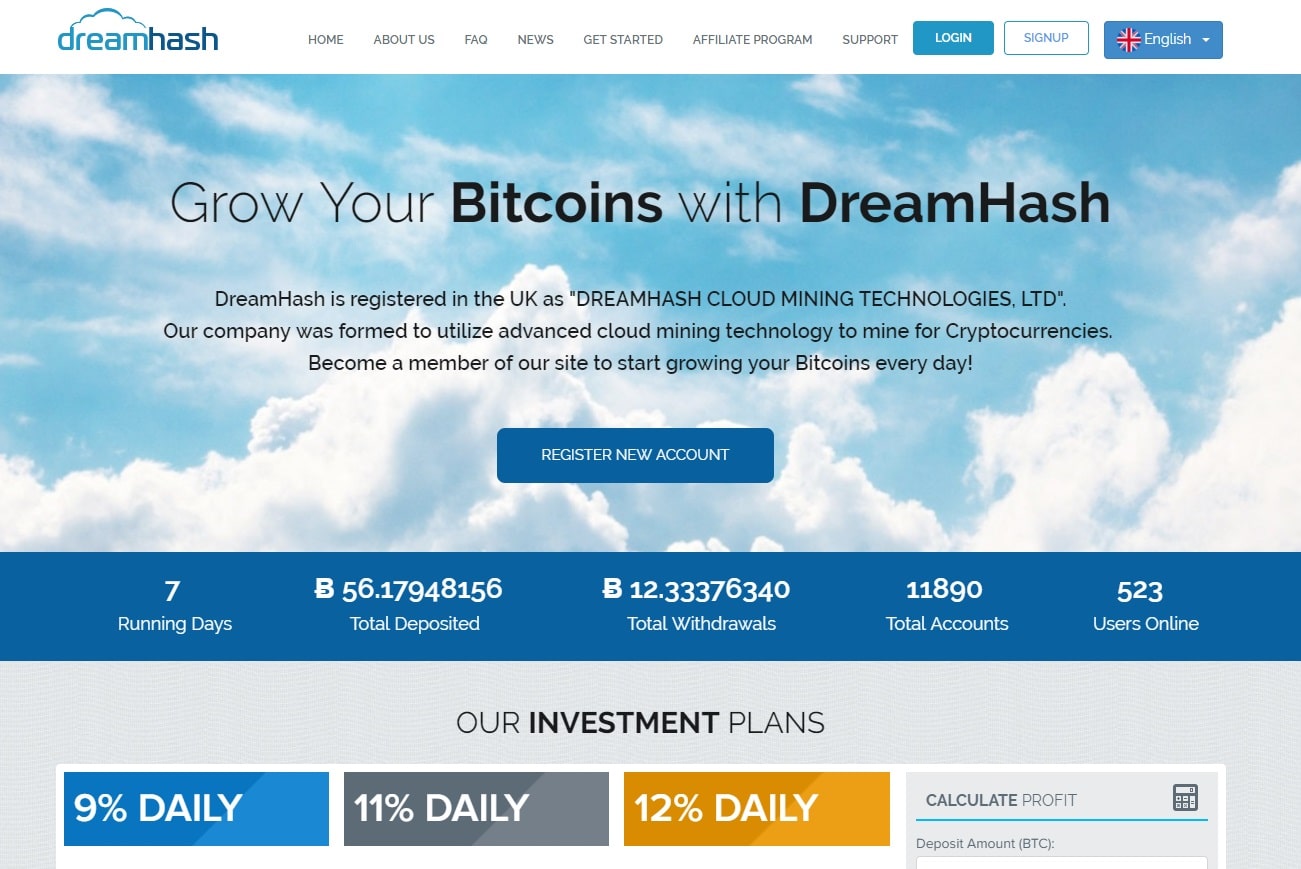
Cloud mining continues to be another popular option for bitcoin schemes. The above-mentioned cryptocurrency scams might appear to be more obvious. In contrast, cloud mining scams often seemingly appear more legitimate. In some cases, cloud mining companies guarantee returns. Again, this is an obvious scam, especially since it’s very difficult to predict cryptocurrency price fluctuation.
Sometimes, fake cloud mining companies are disguised much better and don’t include guarantees on returns. They merely charge users a subscription fee upfront without any real chance of profitability. It’s also worth noting that even the most popular and legitimate cloud mining companies do not offer a good return on investment.
Even if you are thinking about going with a legitimate cloud mining service, it’s important to consider how long it will take you to get a return on investment. Most of the time, it’s easier to make profits via mining rigs or cryptocurrency trading. In any case, always thoroughly read reviews on any cloud mining service.
Don’t Go Phishing
There are few different types of crypto-related phishing scams that anyone should be aware of. First, emails that attempt to fool users into thinking that they are a popular service are commonly scams. For example, a scammer might send a fake security alert saying that someone has just tried to log in to a user’s account. This type of email generally asks a user to click on the link to verify that everything is fine. A scammer can even ask a user to participate in a survey or giveaway by clicking on the link.
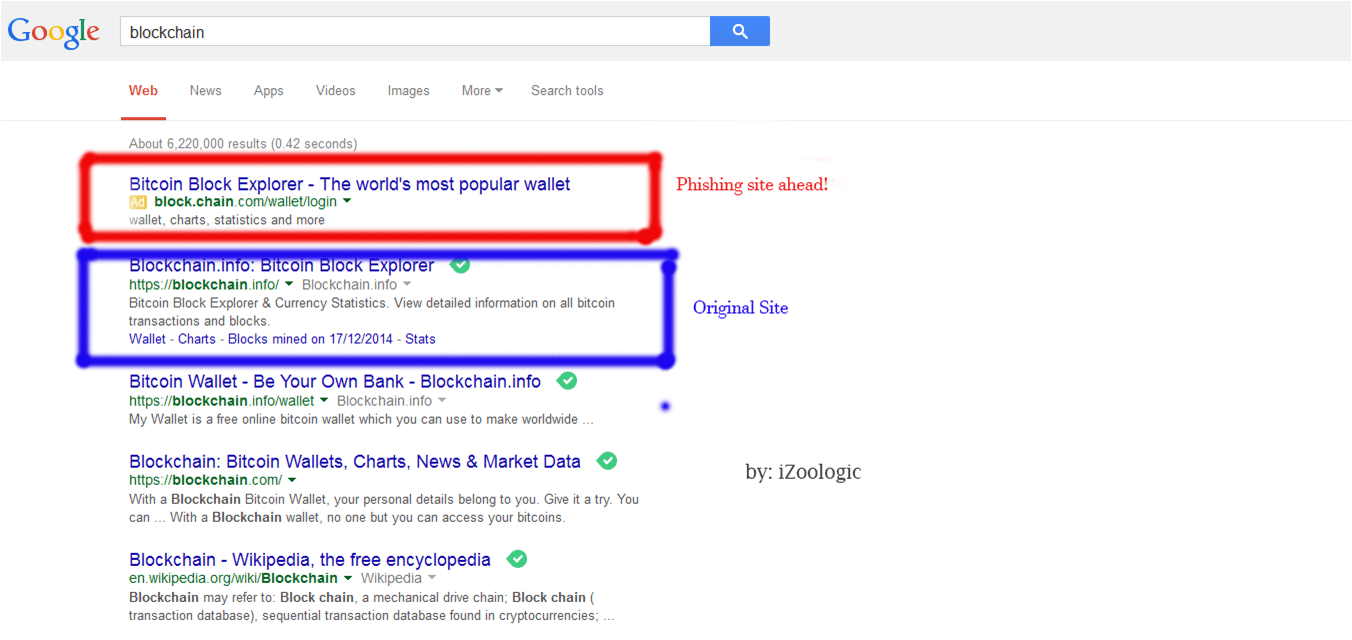
Once a user provides the scammer with sensitive data (i.e. login credentials, private key, etc.), the scammer then has the information needed to hack the user’s account. In some cases, scammers have created Facebook pages and other social media accounts in order to pretend to be a legitimate exchange. Sometimes, scammers even create Google ad campaigns. Always be careful of the outbound links and try to verify that you are going to a legitimate website.
There are a few ways to prevent against phishing attacks. First, it’s always important to make sure that you are going to the correct website. Sometimes, the URL can be similar enough to make you think it is a crypto-site that you use on a regular basis. By verifying that you visit the correct URL every time when entering login credentials, you can keep your funds safe.
Another way to prevent scams is through increased security measures. For example, by enabling two-factor authentication (2FA), you can make it a bit more difficult for hackers to access your actual accounts in case you accidentally fall for a phishing attack. Hopefully, by setting up 2FA, you will be able to increase the security of your funds.
Conclusion
In an age where it is actually possible to become a ‘crypto millionaire’, it’s also important not to think that doing so is easy to accomplish. It should be a top priority for any investor to understand how to prevent from falling for bitcoin schemes. The types of cryptocurrency scams mentioned in this article provide just a few examples of what to watch out for. By using these strategies to detect various scams, it will be simpler to mitigate potential risks and sort out the real opportunities from the fake.
[thrive_leads id=’5219′]
Never Miss Another Opportunity! Get hand selected news & info from our Crypto Experts so you can make educated, informed decisions that directly affect your crypto profits. Subscribe to CoinCentral free newsletter now.










