- What is Binance DeFi?
- The Binance Decentralized Exchange (DEX)
- Staking on the Binance Smart Chain
- The BNB Token’s Role in DeFi
- Final Thoughts: Is Binance DeFi Legit?
Binance is a powerhouse with upwards of 15 million users (up to three million active on the platform daily) and is responsible for around $40 billion in daily trade volume.
Binance is regarded as one of the most powerful companies in the cryptocurrency industry, albeit a controversial past. As a centralized company with a semi-controversial past, Binance’s DeFi entrance was met with polarizing mixed opinions.
Proponents welcomed Binance as an alternative to Ethereum’s exorbitant gas prices, which tickled upwards of $150 per transaction.
Critics were put off by the fact that Binance’s “DeFi” play is still completely centralized, viewing the company’s corporate structure as a threat to the DeFi community’s decentralized ethos.
Let’s explore both sides and how DeFi works on the Binance platform.
What is Binance DeFi?
The Binance Smart Chain is its own chain, and isn’t a layer 2 solution on top of the current Binance mainnet; it’s built to be a stand-alone product designed with the “financial freedom” ethos of DeFi, while positioning Binance, a centralized exchange, favorably in the growing DeFi ecosystem.
Editor’s note: although Binance’s DeFi isn’t decentralized, we’ve continued to use “DeFi” when describing the suite of Binance products. Don’t get lost or riled up in the semantics.
The Binance Smart Chain itself is at least non-custodial, meaning that it doesn’t take custody of user assets. Binance DeFi hosts a suite of developer tools to encourage innovation for the sake of offering everyday users an approachable means to interact with a DeFi ecosystem. The Binance DeFi ecosystem comes with:
- a Decentralized Exchange (DEX)
- an option to stake cryptocurrencies
- the ability to build dApps, similar to the Ethereum Virtual Machine.
The Binance Decentralized Exchange (DEX)
The availability of “reliable liquidity” is a significant issue plaguing decentralized exchanges.
Slippage is another pesky DEX problem; it happens when traders are forced to settle for different prices due to market movements before settling the trade. It’s hard to justify using a DEX over a centralized exchange or prime brokerage when moving large amounts of tokens.
The Binance DEX aims to help users transact large trading volumes at scale. The DEX can function as a fiat on or off-ramp, based on regulations in the user’s region. Users can also purchase cryptocurrency with Visa and Mastercard credit/debit cards.
The DEX allows users to represent Ethereum-based ERC20 tokens in the ecosystem via binding. Binding is the process that enables tokens to be traded cross-chain (i.e., between the Binance Smart Chain or another blockchain.) Binded tokens can be represented on the BSC.
Binding requires interacting with Binance’s TokenManager contract. The owner of the BEP20 token address must:
- Use something like MyEtherWallet to call the approval of the token to the TokenManager contract.
- Then, in myetherwallet, call approveBind in the TokenManager contract to approve the bind request from the BEP20 owner address.
- Approve the bind on the Binance Chain.
Crosschain interoperability locks value in a smart contract and then represents it as a token on the other chain, and scarcity is maintained.
Tokens from ETH are locked via smart contracts to the BSC.
Staking on the Binance Smart Chain
Blocks are produced by validators on the BSC.
Validators are the people who have paid the cost for software and hardware to run a node– the costs include a minimum of 10,000 BNB for self staking and a PC with the following minimum specs- a CPU with 8 cores and 16GB of RAM 500 SSD storage.
Delegators are users who stake meaningful amounts of BNB; they decide on the current rotation of validators. Users can automatically stake their BNB just by holding BNB tokens on the Binance exchange on the main Binance Chain. To participate in the DeFi version, a delegator must choose a validator from the list of available validators on the website to earn rewards from the system.
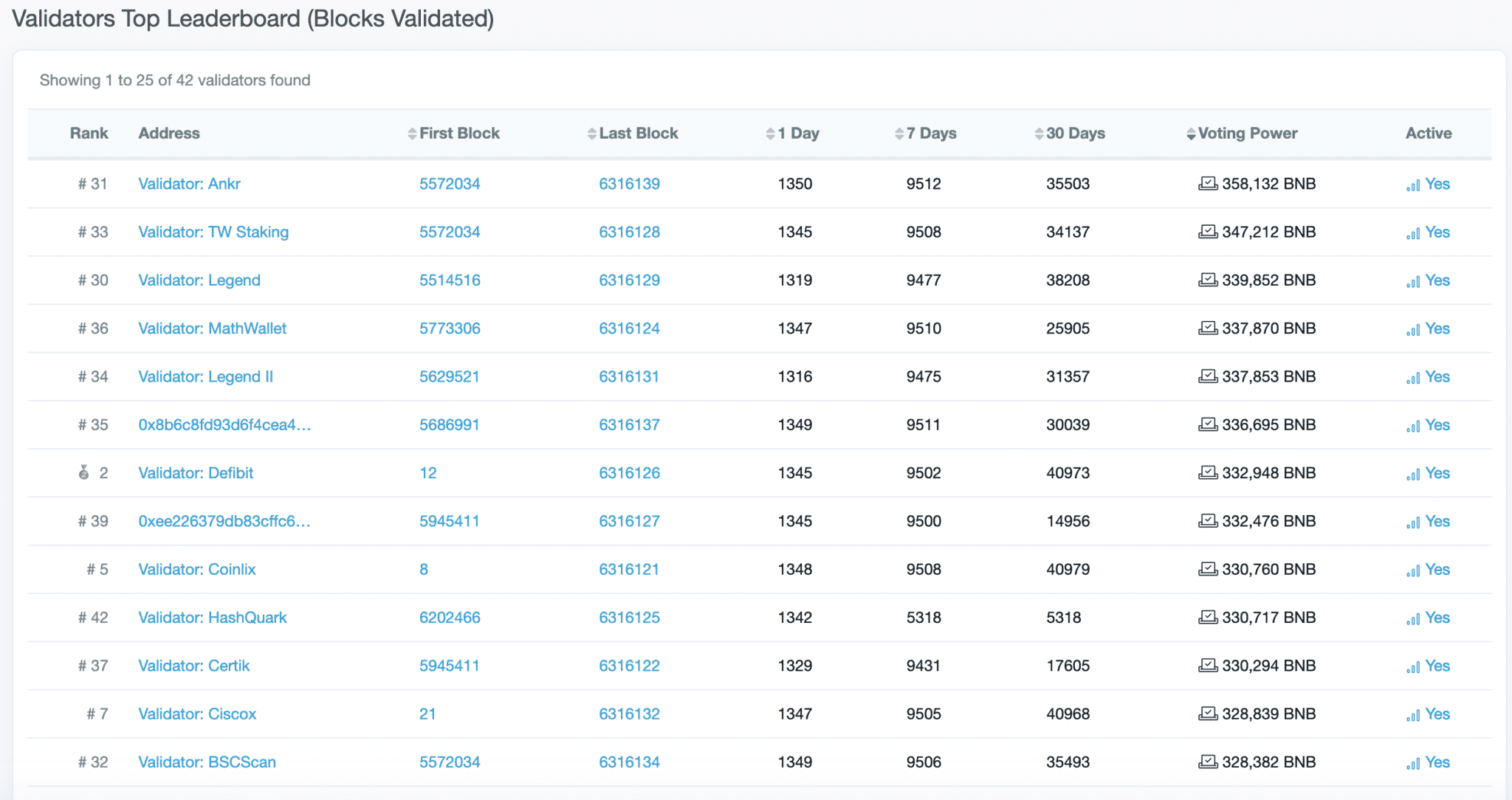
With the BSC’s Proof of Staked Authority (PoSA) system, validators and block producers have an equal opportunity to earn fees. This happens because validators are rotated and the system that determines the rotation is driven by the delegators who vote with their BNB coin allocation.
Therefore, validators must attract delegators to choose to stake their BNB with them.
Fees are issued to validators who in turn give a percentage to the delegators. When chosen, the stake is locked for 7 days. In theory, if a validator is too greedy and does not distribute enough fees, they would be voted out based on the loss of staking value. A gain or loss of stake is generally what the BSC uses as a measurement of trust.
So, a validator must attract and keep the delegator’s vote by preventing slashing events and distributing enough fees to make staking attractive.
The distribution of staking rewards is delayed by two days and delegators receive their funds first, with the remains being transferred to the validators. As such, validators are incentivized to perform their job honestly without the need for manual enforcement by a central entity.
Binance staking rewards are distributed on the BC every day at approximately UTC 00:00.
Building a dApp on the Binance Smart Chain
In traditional finance, institutions develop permissioned tools to operate in the market, and access is usually limited to company employees.
Users in the cryptocurrency industry want total, or at least a majority, of control over the tools used to access the market.
There are over a hundred decentralized apps (dApps) on the Binance Smart Chain. Developers can build their own tools to interact with the BSC, determining their own rules for how users interact with markets.
Currently, over 180 projects are hosted on the chain as Dapps. There are no forms of support available for listed projects. Therefore, do your own research before locking any tokens on the platform.
The BNB Token’s Role in DeFi
Despite the growth of the Binance ecosystem,
The BNB token is deflationary–only 200M BNB has ever been made, and burnings of the token happen regularly.
Logically, due to the lack of inflation, the price of the BNB token will likely increase as the BNB is used, locked, burnt, or otherwise consumed.
Final Thoughts: Is Binance DeFi Legit?
The DeFi community at large seems to be very protective of the DeFi narrative.
Open-source software allowed major systems to become interoperable and compatible. As shown in software development, when there is open software, systems are easily integrated and players can communicate openly.
Innovation is therefore a by-product of an environment that encourages freedom, rather than restricting it.
As the DeFi ecosystem evolves, projects like BSC and ETH will likely become more compatible, making the tools more accessible for everyone.
DeFi still seems to be far from reaching a mainstream base of users. However, the pace of innovation may produce a much more user-friendly DeFi product in the future. When the retail public finally interacts with DeFi, they may not even know they’re using a blockchain-based platform.
The blockchain allows for decentralized money native to the Internet, which can be programmed to represent anything a user wants, whether that be a house or an NFT of a cat. Imagine being able to take out a loan with a CryptoKitty as collateral.
DeFi gives blockchain innovation a palpable focus.
Binance’s DeFi play is notable because it brings the advantages of a centralized platform to innovate in a decentralized ecosystem; it has the resources, coordinated focus, and an internal united army of developers to accomplish its goals.
However, the stigma associated with its centralization has strengthened Ethereum maximalists’ conviction, as well as encouraging innovation in other DeFi ecosystems.
Never Miss Another Opportunity! Get hand selected news & info from our Crypto Experts so you can make educated, informed decisions that directly affect your crypto profits. Subscribe to CoinCentral free newsletter now.