According to the Satis Group, 80 percent of ICOs turn out to be scams. While it’s true you need to be careful about where you send your Ether, keep in mind that the ICO space is still very young. 9 out of 10 of all startups don’t stay the distance either, that’s just par for the course. When assessing blockchain solar energy startups, the greatest indicator of a project’s success lies in its community, backers, and real, viable working use cases.
Blockchain Solar Energy Startups Are Not Immune to Marketing Hype
A quick search for blockchain solar energy startups tends to find the same names cropping up with promises of changing the world. While some of these may be true, just as with any ICO, they could also be empty words backed up by an astute PR team.
So with blockchain solar energy startups, examine the project’s viability. How will it be used and by whom? Who are the people behind the idea, and what experience do they have? Are there any actual projects you can see or code you can check on Github?
As noble a cause as renewable energy may be, there were 122 blockchain startups in the energy space as of March 2018, with new ones appearing every week. Blockchain energy startups raised $322 million between Q2 2017 and Q1 2018. It’s becoming known that a popular cause and a buzzword technology catch investors’ attention.
Many blockchain solar energy startups may go the distance. But it’s still too early to tell which one will conquer the space. So let’s take a look at some of the most important blockchain solar energy startups so far–and why they stand out from the rest.
1. SolarCoin
No article about blockchain solar energy startups would be complete without talking about SolarCoin first. Launched in 2014, the idea behind SolarCoin is to be a rewards program for solar electricity generation. One SolarCoin equals one megawatt-hour of solar energy production.
Self-proclaimed as the “air-miles” for solar electricity generation, SolarCoin is specifically targeted at individual households who install solar panels in their roofs and commercial solar electricity producers. SolarCoin aims to provide the incentivization that is missing to produce more solar electricity globally.
Installing a solar panel can be costly and SolarCoin helps to reduce the payback time for doing so. SolarCoin has become an accepted and respected name in the industry, helping to create jobs in the sector and working with other blockchain startups, including ElectriCChain.
However, since many countries reduced their subsidies for solar power, solar energy has lost its popularity a little. In January 2014, SolarCoin had supported transactions over $2.1 million and was among the top 50 cryptocurrencies. But now its value is low, hovering around the 430th position on CoinmarketCap.
2. Sun Exchange
This blockchain solar energy startup has been around for a few years and already seen demonstrable success, raising $1.6 million in seed funding last year. Sun Exchange talks about “solar-powered money” and, unlike other startups, is not a peer-to-peer solar energy trading platform. In fact, the company does not trade power but instead crowdfunds solar projects around the globe.
They have several successful projects already completed, including building solar panel roofs in African schools and elephant reserves. Through Sun Exchange, you can purchase “solar cells” that you can allocate to the project of your choice from one on their website. You can also suggest projects that you would like to see funded.
Particularly noteworthy about the Sun Exchange is the list of successful projects behind them, and their experienced team, and affiliates. Among their partners, you’ll find Barclays, Energy Web Foundation, and the UN.
3. Conjoule
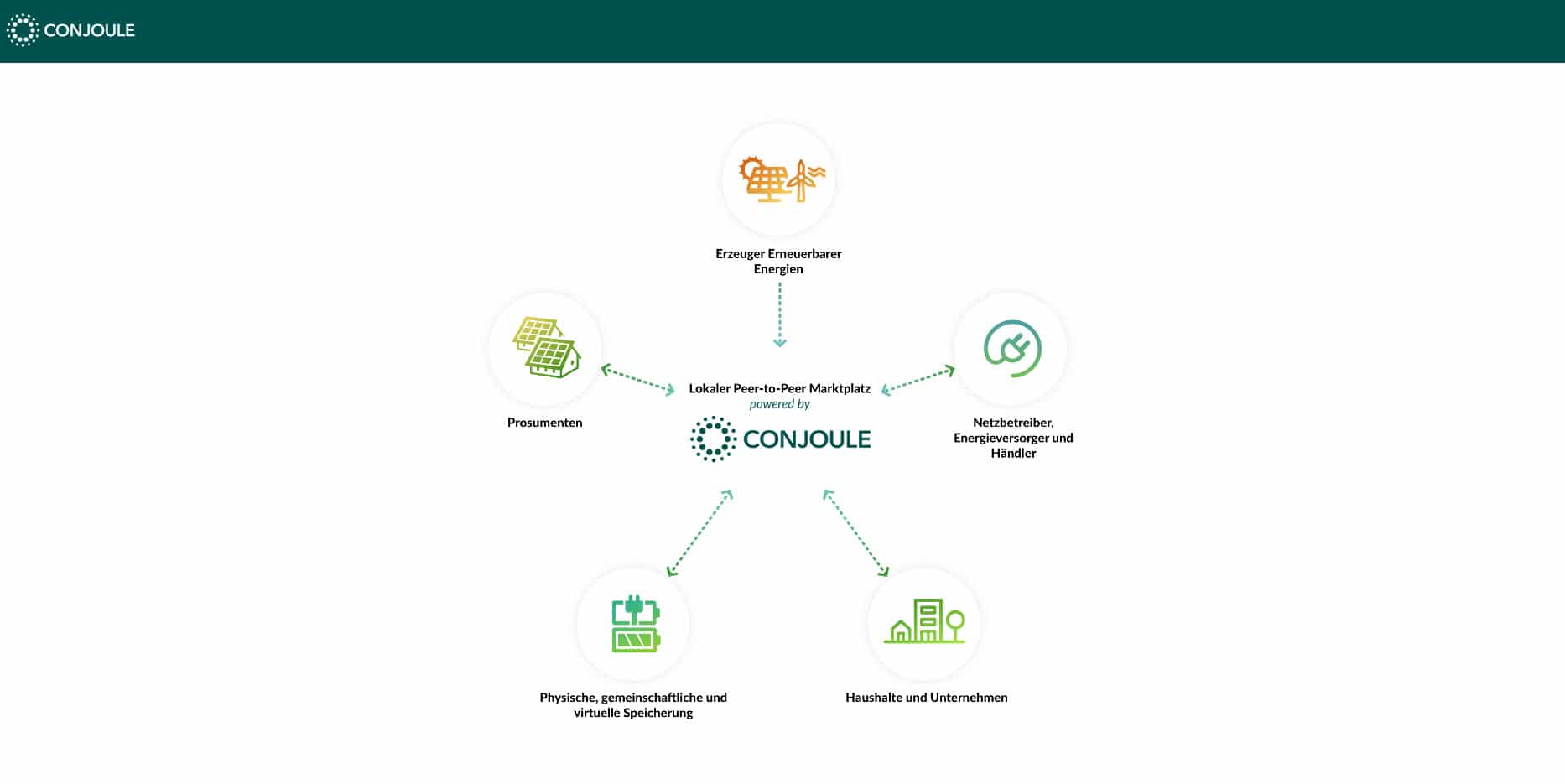
German-based Conjoule supports peer-to-peer trading of solar energy between rooftop PV owners, but also between corporate buyers and interested public-sector members. With significant backing from large names, and $5.3 million from investors including the Tokyo Electric Power Company in July of 2017, this blockchain startup didn’t hold an ICO.
Japanese companies are often associated with being forward-thinking. The Tokyo Electric Power Company is no different, taking a major stake in this energy trading platform. They see a growing demand for peer-to-peer energy transactions in Japan in particular, as this type of incentivization system creates involvement in local production for local consumption.
Conjoule is also developing a prototype for other types of renewable energy, including wind, but their main focus is on blockchain solar energy for now.
4. LO3 Energy
New York-based LO3 Energy is a blockchain solar energy startup with a lofty goal. They aim to revolutionize how energy is generated, stored, traded and consumed at local levels through the blockchain. And they’ve caught the eye of tech behemoth Siemens.
Renowned for its engineering excellence, Siemens will be assisting LO3 Energy to design and build microgrids through blockchain that allow for local energy trading. LO3 was, in fact, the first project to aim for energy trading on a local level.
Their pilot microgrid in Brooklyn is impressive, involving the whole community, as well as their Enexa grid in Southern Australia, and Allgau Microgrid Project in Germany. The microgrid system can operate in a standalone fashion, as well. This means that in the event of a disaster, people can still receive power.
5. WePower
WePower is another important blockchain based green energy trading platform. WePower works with blockchain solar energy systems and other forms of renewable energy as well.
Allowing for peer to peer energy credit trading, the company borrowed the idea from existing solar incentive models. Many residential customers who installed solar panels are already incentivized. This is usually in the form of a cheaper bill, in a process called ‘metering.’
Now they can sell their surplus for WPR tokens. Each token represents one kilowatt-hour of power and is tradable on the platform.
WePower’s primary focus is on larger renewable energy producers of solar, hydro, and wind. The company already claims to have a 1 gigawatt capacity in place with three solar plants in Spain. But it will be open to individual producers as well, making power tradable, cheaper, and accessible by anyone.
Closing Thoughts
There are many important blockchain solar energy startups, and far too many to name in one article. But even though blockchain has become the new buzzword for many an industry, it’s actually proving to lend itself particularly well to the energy sector.
Just remember to look beyond the long words and elaborate proposals to a real, workable project and solid protocol behind it.
[thrive_leads id=’5219′]






